3k+Uploads
10009k+Views
11617k+Downloads
Mathematics

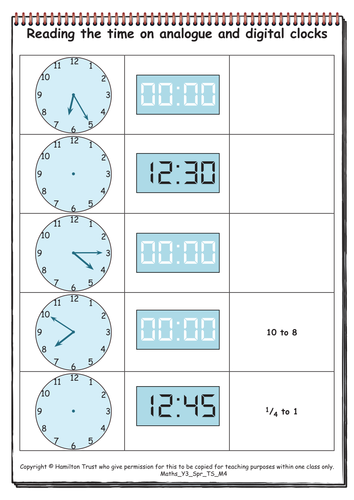
Maths Y3 Spring Teaching Sequence M4
Time, reading digital and analogue clocks (minutes past and to) (three days).
Children revise the equivalent digital and analogue ways of recording times between the hour and half past the hour (minutes past), and are then introduced to how to describe analogue times as minutes to the next hour. They practise finding the equivalent digital and analogue times. Intervals are found between times, but not bridging the hour at this point. Chn work together to think of times 20 minutes, then 1¼ hours apart.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

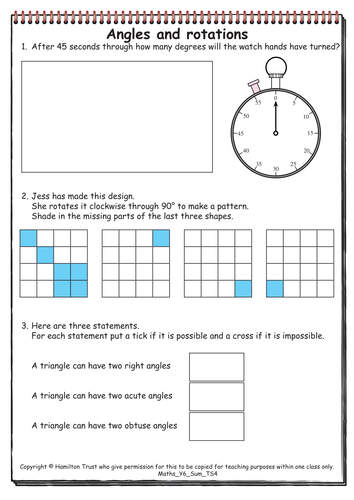
Maths Y6 Summer Teaching Sequence 4
Revision: Shape (two days).
Children discuss turns of multiples of 90° on the clock face, and rotate shapes through 90°. They sort shapes according to their properties, e.g. number of right angles, obtuse angles, acute angles, lines of symmetry, and pairs of parallel sides. They practise measuring angles accurately with a protractor.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

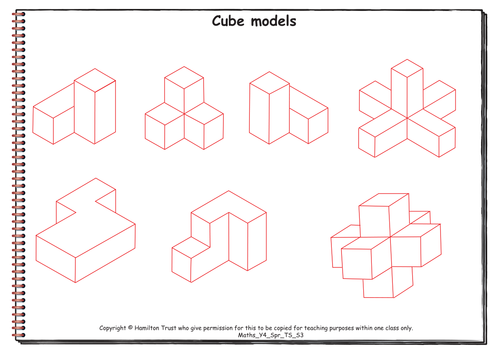
Maths Y4 Spring Teaching Sequence S3
Properties of 3D solids (three days).
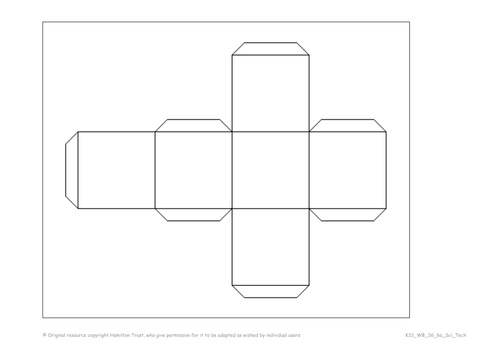
Children revise the names and properties of 3D solids and learn the name and properties of the tetrahedron. Straws are used to make skeletons of 3D shapes, reinforcing the numbers of edges and vertices. Children investigate which nets will make a cube and investigate nets of other shapes including packaging.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

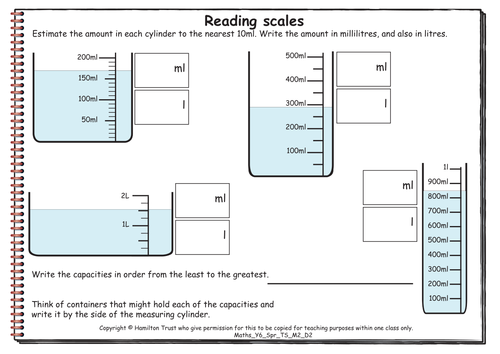
Maths Y6 Spring Teaching Sequence M2-D2
Measures and handling data: range, mode, mean and median (five days).
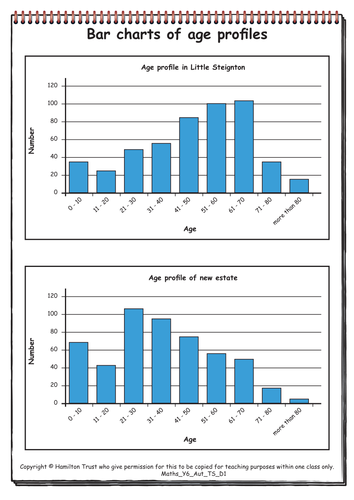
Children read a variety of scales, including those where the measure comes to a point between divisions. They record the measurements in millilitres and litres (to two decimal places) or grams and kilograms (to two decimal places). Children are asked whether they think Year 1 and year 6 children make different school meal choices, data is collected and shown in both bar charts and pie charts. Children write about what these graphs tell them. Data is collected about the number of letters in children’s names; the data is grouped and presented in bar charts. Different forms of average are found (mean, mode and median) and also the range between the shortest and the longest names. Line graphs are drawn to show the conversions between inches and centimetres and grams and ounces. These graphs are used to derive more facts.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

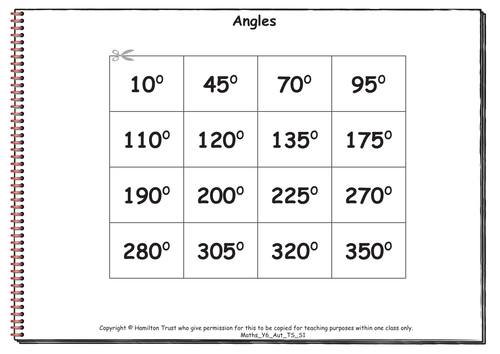
Maths Y6 Autumn Teaching Sequence S1
2D and 3D shape and angles (five days).
Children identify and draw acute, obtuse and reflex angles. They use the fact that angles in a triangle add up 180° to work out missing angles. Children draw 2D shapes according to given properties. Quadrilaterals including kite, rhombus, trapezium and parallelogram are introduced and children sort them according to their properties including pairs of parallel sides. Children identify nets of closed cubes and make other 3D solids, recording their properties including pairs of parallel faces.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

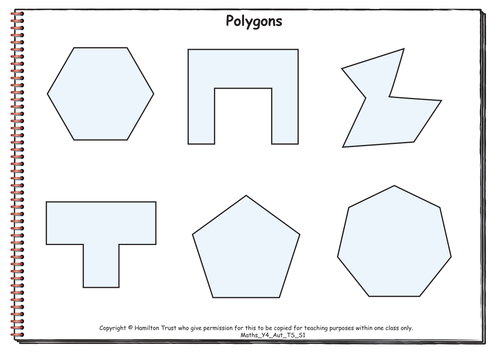
Maths Y4 Autumn Teaching Sequence S1
Symmetry and properties of 2D shapes (five days).
Children learn the name heptagon and draw as many different looking heptagons as they can. They name and describe a range of polygons, for example if they regular or irregular, symmetrical or not, have right angles or not. The terms equilateral and isosceles are introduced; children sort triangles according to their properties and use equilateral and right-angled triangles to make symmetrical patterns. They imagine and draw polygons and investigate the numbers of lines of symmetry particular polygons can have, reaching a generalisation. They create patterns with one then two lines of symmetry.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

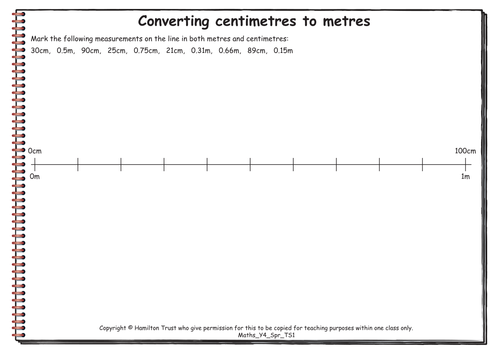
Maths Y4 Spring Teaching Sequence 1
Decimal notation for tenths and hundredths (three days).
Children learn to write distances of less than 100cm as metres, discussing the value of each digit. They move onto convert distances of more than 100cm from centimetres to metres, ordering measurements and using a number line to help. Results (times to the nearest hundredth of a second) of Olympic events are then compared and athletes’ positions worked out.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

Shopping Basket
Look at products that would be on weekly shopping list, consider the different ways in which these were sold – less packaging. Discuss equivalents between imperial and metric measurements and money. Children convert prices or sort foods into then and now.

Maths Y4 Spring Teaching Sequence 7
Add/subtract near multiples of 10/100, Use negative numbers in context, Read scales (four days).
Children use counting on and back in 10s or 100s and adjusting to add and subtract near multiples of 10 or 100. They use ENL jottings to help, particularly when crossing multiples of 100 and 1000. Negative numbers are introduced in the context of temperature, negative numbers are compared and simple differences in temperature found. Children read and mark numbers on different scales.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

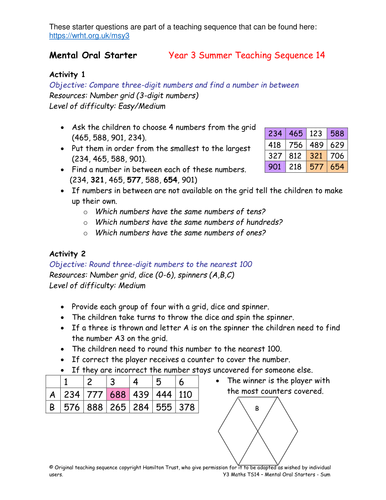
Mental Oral Starters - Year 3
Mental and oral starters for Year 3 Summer Teaching Sequence 14.
Compare three-digit numbers and find a number in between. Round three-digit numbers to the nearest 100. Find 20, 30, …90, 100, 200, 300 more/less than three-digit numbers. Use pairs to ten to find complements to 100. Understand multiplication is commutative and find remainders after division. Use multiplication facts for the 2, 3, 4, 5, 9 and 10 times tables. Find ½, ¼, ¾, 1/10s, 1/8s and several tenths/eighths of numbers.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

Infant Maths Leaflet
A leaflet for parents which outlines the type of Maths being taught in Key Stage 1 classrooms.

Maths Y6 Autumn Teaching Sequence D1
Handling data: frequency tables, bar charts, pie charts and line graphs (four days).
Grouped data is used in frequency tables and bar charts. Children draw line graphs and read intermediate points. They match stories to line graphs and write their own stories to accompany line graphs. Children learn how to construct, interpret and compare simple pie charts.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

Maths Y5 Spring Teaching Sequence S2
Classifying 2D and 3D shapes (five days).
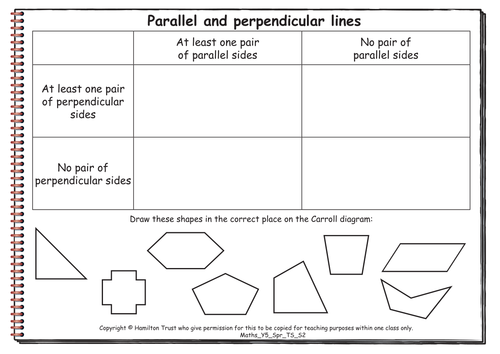
Children learn to use the words ‘parallel’ and ’perpendicular’ to describe pairs of lines, and then make and sort shapes according to whether they have perpendicular or parallel sides or both, using Carroll diagrams to record their results. Chn find the number of axes of symmetry in regular and irregular 2D shapes. They sort and make 3D shapes including open cubes and prisms, but also more complex polyhedra.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

Maths Y3 Spring Teaching Sequence 12
Ordering and finding fractions of shapes and numbers (three days).
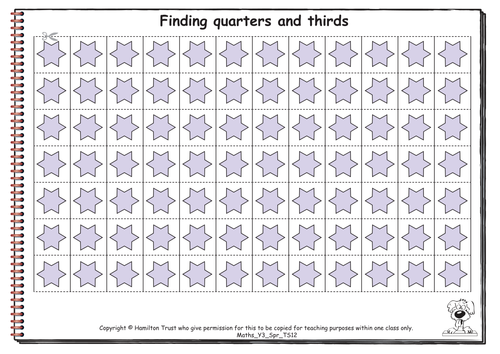
Children revise find halves, quarters and thirds of strips of objects and then identify the fraction of objects that is ringed. Tenths are introduced, chn order halves, quarters and tenths on a number line and then find tenths and thirds of numbers, linking finding a fraction to the sharing image of division. The link between sharing and grouping is discussed, so that children can use grouping and their division facts to help find a fraction of a number.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

Make A Box
Moving on from the last session, children explore how boxes are made from nets by taking apart packaging boxes. Then using a pre-prepared net, children make and design their own boxes.

Mental Oral Starters - Year 1
A bank of starters available for Maths. Teaching Sequences refer to starters relating to Teaching.
Name five 2-d shapes, recognise their properties. Read and write numerals to match number words. Name 2-d shapes, recognise and extend a repeating pattern. Add by counting on, putting the larger number first. Recognise coins up to £2.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

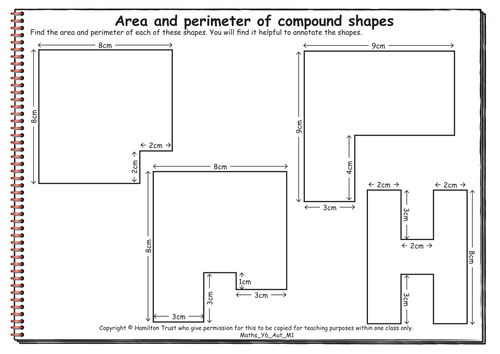
Maths Y6 Autumn Teaching Sequence M1
Measures: area and perimeter (four days).
Children use a formula to find the area of rectangles, and then divide up compound shapes into rectangles to find their area. They learn how to find the area of right-angled triangles, and use this to find areas of compound shapes that can be divided into rectangles and triangles. They also find the perimeters of rectangles and compound shapes. Drawing round objects on squared paper, counting squares and taking account of partial squares is used to find the area of handprints and leaves.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

Maths Y5 Spring Teaching Sequence 5
Fractions, Decimals, Percentages, Ratio and proportion (five days).

Maths Y6 Summer Teaching Sequence 15 Special
Maths in art and nature (five days).
Children make their own tessellating patterns. Starting with a simple design they use rotations, reflections and translations to make different patterns. They draw fractals beginning with an equilateral triangle. The Golden Section is introduced, and this links with the Fibonacci sequence, examples in nature and architecture pointed out and children find pairs of body measurements with this ratio.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.

Maths Y6 Spring Teaching Sequence S2
Co-ordinates, translations, rotations and transformations (five days).
Children complete shapes and reflect shapes on grids, giving their coordinates. Shapes are moved, the translations described and new coordinates found. Children rotate shapes on grids and design them to form patterns. Four quadrants are introduced.
Find additional lesson plans and resources at www.hamilton-trust.org.uk.